Filter Node
Purpose & Use Cases
The filter node applies various image processing filters for enhancement, artistic effects, and image analysis. It provides optimized implementations of common filters including blur, sharpen, edge detection, emboss, and Gaussian operations.
Real-World Applications:
- Photo Enhancement: Sharpen portraits and improve image quality
- Artistic Effects: Create stylized images with emboss and edge effects
- Quality Control: Use edge detection to analyze product shapes and boundaries
- Medical Imaging: Enhance contrast and details in diagnostic images
- Preprocessing: Prepare images for AI analysis with noise reduction and enhancement
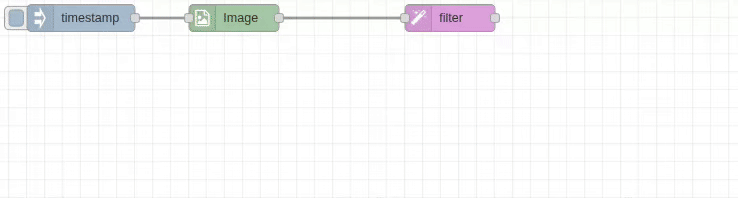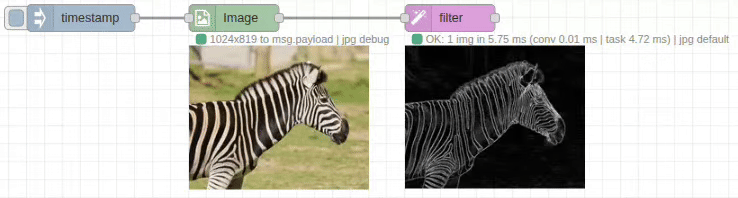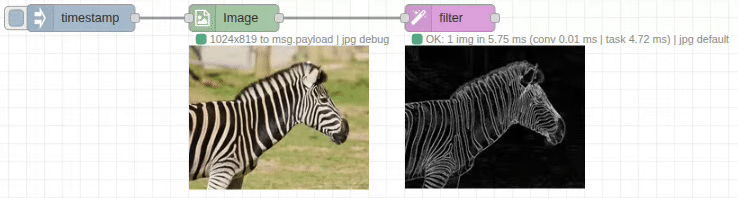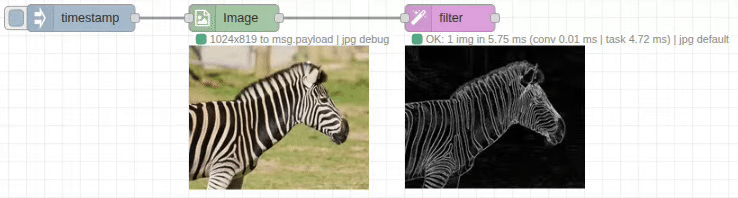
Input/Output Specification
Inputs
- Single Image: Standard image object format
- Image Array: Array of image objects for batch filtering
- Dynamic Parameters: Filter strength and settings via message properties
Outputs
- Filtered Image: Image with applied filter effects
- Preserved Dimensions: Output maintains original image dimensions
- Format Options: Raw image object or encoded file formats
Configuration Options
Input/Output Paths
- Input From:
msg.payload(default),flow.*,global.* - Output To:
msg.payload(default),flow.*,global.*
Filter Types
Blur Filter
- Purpose: Reduces image noise and creates soft focus effects
- Strength: Configurable blur radius
- Use Cases: Noise reduction, background softening, privacy protection
Sharpen Filter
- Purpose: Enhances image details and edge definition
- Strength: Configurable sharpening intensity
- Use Cases: Photo enhancement, print preparation, detail emphasis
Edge Detection
- Purpose: Highlights edges and boundaries in images
- Output: Binary or grayscale edge maps
- Use Cases: Object detection, shape analysis, contour extraction
Emboss Filter
- Purpose: Creates 3D relief effect with depth appearance
- Direction: Configurable embossing direction
- Use Cases: Artistic effects, texture analysis, decorative processing
Gaussian Blur
- Purpose: Smooth blur with natural falloff
- Sigma: Configurable standard deviation for blur amount
- Use Cases: Background blur, noise reduction, preprocessing
Filter Strength/Parameters
- Range: Varies by filter type
- Sources: Number,
msg.*,flow.*,global.* - Dynamic: Runtime adjustment via message properties
Output Format Options
- Raw: Standard image object (fastest for processing chains)
- JPEG: Compressed with quality control
- PNG: Lossless preservation of filter effects
- WebP: Modern format with excellent compression
Performance Notes
C++ Backend Processing
- Optimized Kernels: Hand-tuned convolution implementations
- OpenCV Integration: Leverages OpenCV's optimized filter functions
- Memory Efficient: In-place processing where possible
- Parallel Execution: Multi-threaded processing for large images
Filter-Specific Performance
- Blur/Gaussian: Linear time complexity with kernel size
- Sharpen: Fast single-pass convolution
- Edge Detection: Sobel or Canny edge detection algorithms
- Emboss: Single convolution pass with directional kernel