Padding Node
Purpose & Use Cases
The padding node adds margins around images with configurable colors and dimensions. It expands the canvas size while preserving the original image content, perfect for creating borders, standardizing dimensions, or preparing images for specific layouts.
Real-World Applications:
- Social Media Formatting: Add borders for consistent post dimensions
- Print Preparation: Add bleed areas and margins for professional printing
- Gallery Display: Create uniform frames for image collections
- Logo Branding: Add branded borders around product images
- Document Layout: Add margins for text overlay or annotations
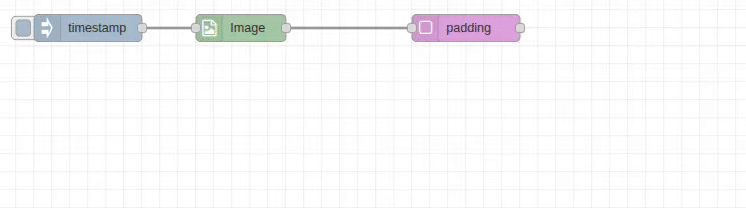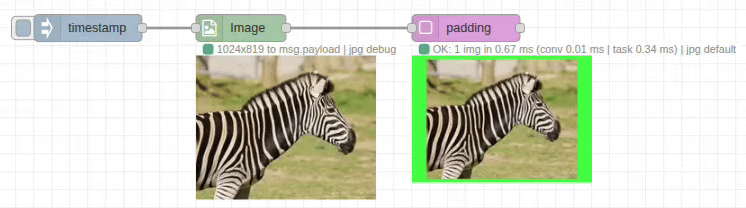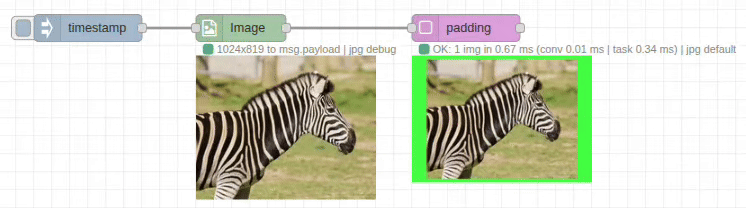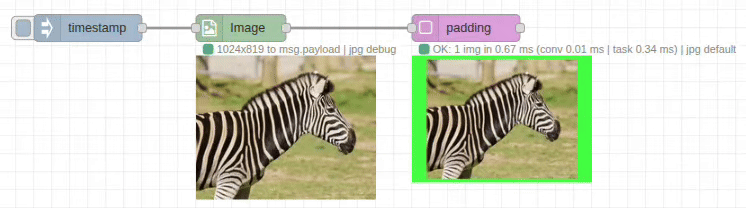
Input/Output Specification
Inputs
- Single Image: Standard image object format
- Image Array: Array of image objects for batch padding
- Dynamic Values: Padding dimensions can be provided via message properties
Outputs
- Padded Image: Original image with added margins
- Expanded Dimensions: Canvas size increased by padding amounts
- Format Options: Raw image object or encoded file formats
Configuration Options
Input/Output Paths
- Input From:
msg.payload(default),flow.*,global.* - Output To:
msg.payload(default),flow.*,global.*
Padding Dimensions
Top Padding
- Type: Pixels (integer)
- Sources: Number,
msg.*,flow.*,global.* - Effect: Adds space above the image
Right Padding
- Type: Pixels (integer)
- Sources: Number,
msg.*,flow.*,global.* - Effect: Adds space to the right of the image
Bottom Padding
- Type: Pixels (integer)
- Sources: Number,
msg.*,flow.*,global.* - Effect: Adds space below the image
Left Padding
- Type: Pixels (integer)
- Sources: Number,
msg.*,flow.*,global.* - Effect: Adds space to the left of the image
Color Configuration
Padding Color
- Formats Supported:
- RGB:
rgb(255,0,0),rgb(255,255,255)
- RGB:
- Default: Black
Output Format Options
- Raw: Standard image object (fastest for processing chains)
- JPEG: Compressed (note: transparency becomes white)
- PNG: Lossless with full transparency support
- WebP: Modern format with transparency support
Performance Notes
C++ Backend Processing
- Efficient Canvas Expansion: Optimized memory allocation for padded dimensions
- Color Fill: Fast uniform color filling using OpenCV
- Memory Management: Minimal memory overhead for padding operations
- Batch Processing: Array inputs processed in parallel
Dimension Calculations
- New Width: Original width + left padding + right padding
- New Height: Original height + top padding + bottom padding
Real-World Examples
Social Media Post Creation
[Image-In: product.jpg] → [Padding: 50px all sides, Brand color] → [Social Post]Add branded borders for consistent social media appearance.
Print Preparation
[Photo] → [Padding: Top=100, Right=50, Bottom=100, Left=50, White] → [Print Ready]Add margins for professional printing with bleed areas.
Gallery Standardization
[Image Array] → [Padding: Equal margins, White] → [Uniform Gallery]Create consistent framing for image galleries.
Logo Watermarking Prep
[Product Image] → [Padding: Bottom=80, White] → [Ready for Logo Overlay]Add space for logo placement with white background.
Document Border Creation
[Document Scan] → [Padding: 20px all sides, Light gray] → [Bordered Document]Add subtle borders to scanned documents.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
Transparency Issues
- Issue: Transparent padding appears white in JPEG
- Solution: Use PNG or WebP format for transparency support
- Workaround: Match padding color to expected background
Large File Sizes
- Issue: Padding significantly increases file size
- Cause: Expanded canvas dimensions
- Solution: Use appropriate compression settings, consider if padding is necessary
Color Matching Problems
- Issue: Padding color doesn't match expected appearance
- Solution: Use exact color specifications (RGB codes)
- Testing: Use debug mode to verify color appearance
Dynamic Dimension Errors
- Issue: Invalid padding values from message properties
- Solution: Validate that dynamic sources contain positive integers
- Safety: Add bounds checking in upstream nodes