Rotate Node
Purpose & Use Cases
The rotate node provides precise image rotation with customizable padding and background colors. It supports both clockwise and counter-clockwise rotation with automatic canvas adjustment to prevent clipping.
Real-World Applications:
- Photo Orientation: Correct camera orientation issues
- Document Processing: Straighten scanned documents and receipts
- Artistic Effects: Create artistic compositions with angled elements
- Quality Control: Align products for consistent photography
- Medical Imaging: Orient medical scans for proper analysis
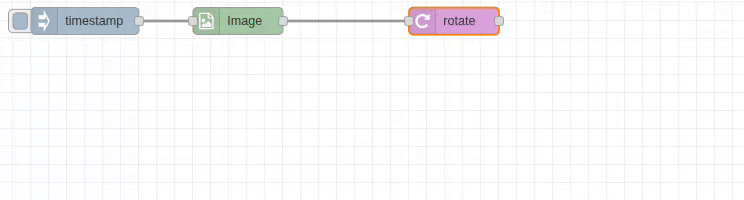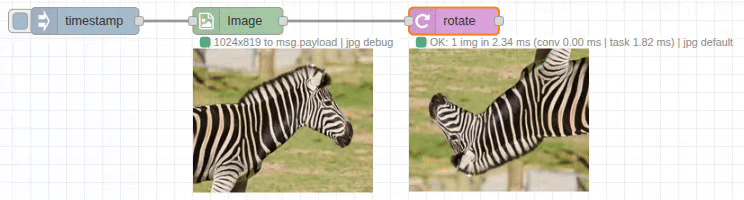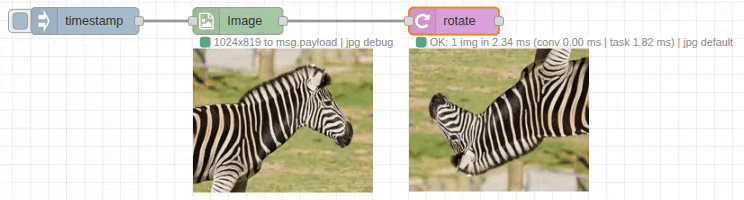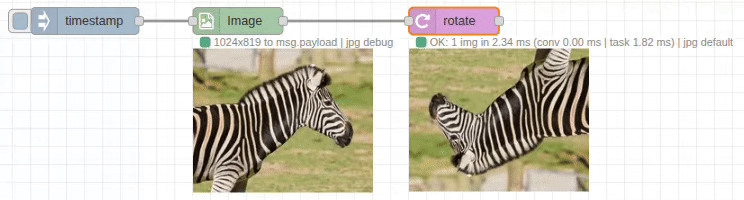
Input/Output Specification
Inputs
- Single Image: Standard image object format
- Image Array: Array of image objects for batch rotation
- Dynamic Angles: Rotation angle can be provided via message properties
Outputs
- Rotated Image: Image rotated by specified angle with expanded canvas
- Format Options: Raw image object or encoded file formats
Configuration Options
Input/Output Paths
- Input From:
msg.payload(default),flow.*,global.* - Output To:
msg.payload(default),flow.*,global.*
Rotation Settings
Angle
- Range: 0-360 degrees (or negative for counter-clockwise)
- Precision: Floating-point precision (e.g., 15.5 degrees)
- Sources: Number,
msg.*,flow.*,global.* - Direction: Positive = clockwise, Negative = counter-clockwise
Padding Settings
- Background Color: Color to fill expanded canvas areas
- Color Formats:
- Hex:
#FF0000(red) - RGB:
rgb(255,0,0) - Named:
red,white,black,transparent
- Hex:
- Default: Black background
Output Format Options
- Raw: Standard image object (fastest for processing chains)
- JPEG: Compressed with quality control (1-100)
- PNG: Lossless with transparency support
- WebP: Modern format with quality control
Performance Notes
C++ Backend Processing
- High-Quality Rotation: Uses OpenCV's optimized rotation algorithms
- Canvas Expansion: Automatic canvas sizing to prevent clipping
- Memory Management: Efficient handling of rotated image dimensions
- Interpolation: High-quality pixel interpolation for smooth results
Processing Characteristics
- Canvas Growth: Output image may be larger than input to accommodate rotation
- Edge Handling: Configurable background fill for exposed areas
- Precision: Sub-pixel accuracy for precise angle control
Real-World Examples
Photo Orientation Correction
[Image-In: rotated_photo.jpg] → [Rotate: -90°] → [Corrected Photo]Fix photos taken with rotated camera orientation.
Document Straightening
[Scanned Document] → [Rotate: 2.3°, White background] → [Straight Document]Correct slight rotation in scanned documents.
Batch Photo Processing
[Photo Array] → [Rotate: msg.orientation] → [Corrected Photos]Apply different rotation angles based on EXIF data.
Artistic Composition
[Logo Image] → [Rotate: 45°, Transparent background] → [Diamond Logo]Create artistic rotated elements with transparency.
Dynamic Rotation
[Analysis] → [Calculate Angle] → [Rotate: msg.correctionAngle] → [Aligned Image]Rotate based on image analysis results.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
Image Size Changes
- Issue: Output image larger than input
- Cause: Canvas expansion to accommodate rotated content
- Expected: Normal behavior to prevent clipping
- Solution: Consider downstream processing for size constraints
Background Color Issues
- Issue: Unexpected background colors in rotated areas
- Solution: Specify appropriate background color for your use case
- Transparency: Use PNG format with transparent background for overlays
Performance with Large Angles
- Issue: Significant rotation (close to 45°, 135°, etc.) creates much larger images
- Optimization: Consider if rotation is necessary or can be minimized
- Memory: Monitor memory usage with very large images
Precision vs. Speed
- Issue: High-precision angles may be slower
- Balance: Use appropriate precision for your requirements
- Optimization: Round to nearest degree if precision not critical